AAV-GCaMP6 was used to investigate whether the IL of the SC receiving somatosensory input reflects visual threat signals. (From
BrainVTA)
The viruses used in this article from BrainVTA are in the table below
|
Calcium sensors |
PT-0110 AAV9-CaMKIIa-GCaMP6-EGFP |
Xuemei Liu, Chen Chen, Yuanming Liu, Zhijie Wang, Kang Huang, Feng Wang and Liping Wang
Pub Date: 2018-10-18,
DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00239,
Email: sales@brainvta.com
Innate defensive responses to threats are essential for animal survival. The complexity and variability of innate defensive behaviors can be due to individual experiences, environmental factors, and internal states. However, it is not completely understood if the gentle handling involved in sensory processing affects innate defensive responses to visual threats. Here, we report attenuation of innate defensive responses after gentle handling accompanied by de-excitation of the intermediate layer (IL) and deep layer (DL) of the superior colliculus (SC) but not of the superficial layer (SL). Our theoretical analysis of the c-Fos network revealed an increased correlation in module 1, which maybe generally functionally associated with fear emotional, a decreased correlation in module 2, which maybe generally functionally associated with sensory processing. The IL of the SC appeared to have the highest correlation with the two modules. We verified the dynamic activities of the IL of SC in response to overhead looming stimulus using fiber photometry. Retrograde labeling of 18 regions of interest (ROIs) showed that the IL received significant inputs from the cortical areas, thalamus, hypothalamus, and brainstem. These data suggest the sensory processing involved in the modulatory roles of the SC in innate fear processing.
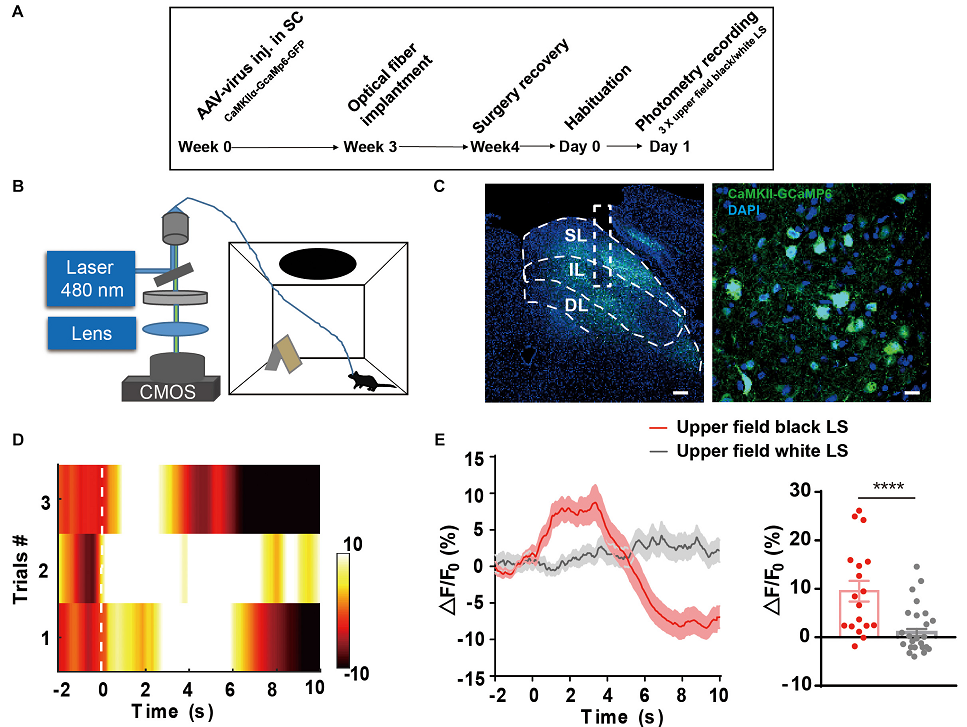
Firure.1 Fiber photometry recording of LS-induced Ca2C transient
In the current study, the authors demonstrated that gentle handling attenuates innate defensive reactions to visual threat stimuli, consistent with findings from previous studies. These studies provide a possibility that gentle handling might change the social interaction with experimenter and animal to improve the animal’s performance. Moreover, it’s possible that gentle handle induced the neurotransmitters such as oxytocin and dopamine release or lower corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) to reduce emotionality, promote calm, and increase the ability to address visual threat situation.
BrainVTA offers viral vector construction & virus packaging services for AAV, LV, RABV, PRV, HSV and VSV that help researchers explore questions about genes, neurons, circuitry structure, function of brain network, mechanism and treatment of diseases.
If you have any needs, just email us at
sales@brainvta.com.
