AAV‐GCaMP6s was used to investigate whether leptin affects the odor‐evoked population activity of M/Ts. AAV‐VGAT1‐CRE was used to record the population calcium signal from genetically labeled granule cells. (All viruses were packaged by
BrainVTA)
The viruses used in this article from BrainVTA are in the table below
|
Calcium sensors |
PT‐0071 AAV‐DIO‐GCaMP6s |
|
CRE Recombinase |
PT‐0346 AAV‐VGAT1‐CRE‐WPRE‐PA |
Pub Date: 2019-06-18,
DOI: 10.1111/apha.13319,
Email: [email protected]
Changcheng Sun, Keke Tang, Jing Wu, Han Xu, Wenfeng Zhang, Tiantian Cao, Yang Zhou, Tian Yu, Anan Li
Aim: Leptin is an important peptide hormone that regulates food intake and plays a crucial role in modulating olfactory function. Although a few previous studies have investigated the effect of leptin on odor perception and discrimination in rodents, research on the neural basis underlying the behavioral changes is lacking. Here we study how leptin affects behavioral performance during a go/no‐go task and how it modulates neural activity of mitral/tufted cells in the olfactory bulb, which plays an important role in odor information processing and representation.
Methods: A go/no‐go odor discrimination task was used in the behavioral test. For in vivo studies, single unit recordings, local field potential recordings and fiber photometry recordings were used. For in vitro studies, we performed patch clamp recordings in the slice of the olfactory bulb.
Results:Behaviorally, leptin affects performance and reaction time in a difficult odor‐discrimination task. Leptin decreases the spontaneous firing of single mitral/tufted cells, decreases the odor‐evoked beta and high gamma local field potential response, and has bidirectional effects on the odor‐evoked responses of single mitral/tufted cells. Leptin also inhibits the population calcium activity in genetically identified mitral/tufted cells and granule cells. Furthermore, in vitro slice recordings reveal that leptin inhibits mitral cell activity through direct modulation of the voltage‐sensitive potassium channel.
Conclusions: The behavioral reduction in odor discrimination observed after leptin administration is likely due to decreased neural activity in mitral/tufted cells, caused by modulation of potassium channels in these cells.
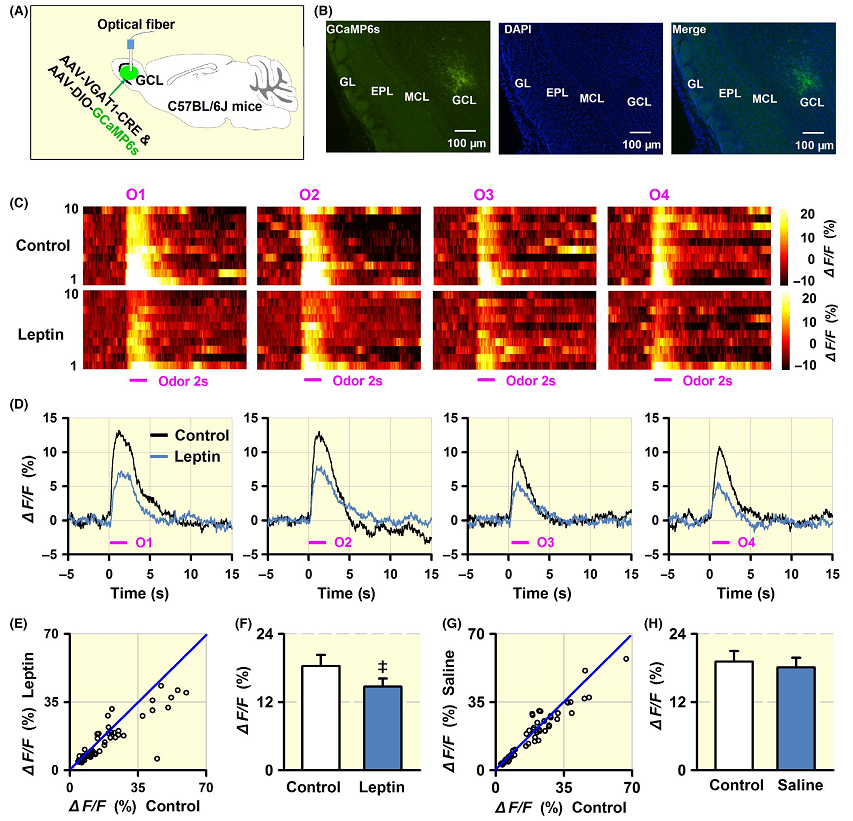 Fig1. Leptin decreases odor‐evoked calcium responses in granule cells.
Fig1. Leptin decreases odor‐evoked calcium responses in granule cells.
In the study, the authors first tested how leptin modulates olfactory discrimination behavior in mice. They then investigated the effect of leptin on the M/Ts of the OB through in vivo electrophysiology and fiber photometry and in vitro patch‐clamp slice recording. They found that leptin modulates olfactory‐guided behavior, likely via decreasing neural activity in the OB M/Ts.
BrainVTA offers viral vector construction & virus packaging services for AAV, LV, RABV, PRV, HSV and VSV that help researchers explore questions about genes, neurons, circuitry structure, function of brain network, mechanism and treatment of diseases.
If you have any needs, just email us at
[email protected].
